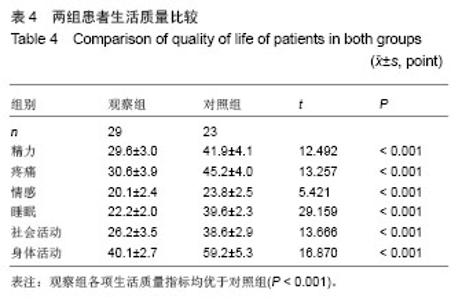
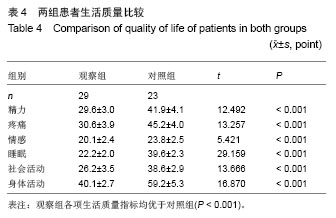
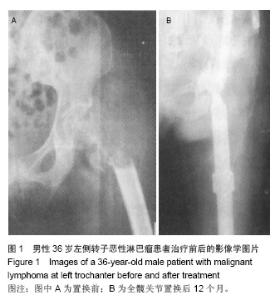
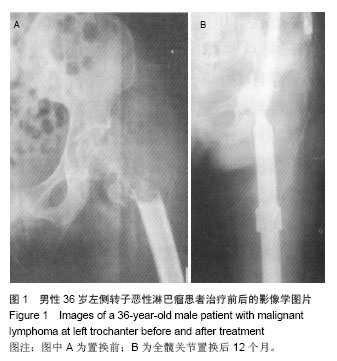
| [1]Raiss P, Kinkel S, Sauter U, et al. Replacement of the proximal humerus with MUTARS tumor endoprostheses. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2010;36(4): 371-377.
[2]Cannon CP, Paraliticci GU, Lin PP, et al. Functional outcome following endoprosthetic reconstruction of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(5): 705-710.
[3]王守丰,熊进,骆东山,等.股骨近端良性骨肿瘤的外科治疗[J]. 江苏医药, 2009, 35(12): 1448-1450.
[4]雷志雄.股骨远端骨肿瘤及肿瘤性病变临床研究[J].当代医学, 2012,18(18):102-103.
[5]杨松华,符彦基,杨丹.股骨近端解剖钢板治疗股骨近端骨折[J]. 中国医疗前沿,2009, 4(9): 32-33.
[6]韩康,杨彤涛,赵新文,等.股骨颈良性骨肿瘤的外科治疗[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2012, 20(4): 808-814.
[7]吴苏稼,施鑫,陆萌.骨与软组织恶性肿瘤误诊误治15例分析[J]. 江苏医药, 2004, 30(2): 153-154.
[8]Tsukiyama I, Ogino T, Egawa S. Hyperthermia for bone and soft tissue sarcoma: Relationship between tomographic and histological findings. Rad Med. 2004;12(5):231.
[9]Moon MS, Woo YK, Lee KS, et al. Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody instrumentation fusion tor tatercalosis kyphosis at thoracic and lumbar spine. Spine. 2005;20(17): 1910-1916.
[10]van de Sande MAJ, Dijkstra S, Taminiau AHM. Proximal humerus reconstruction after tumour resection: biological versus endoprosthetic reconstruction. Int Orthop.2011; 35(9): 1375-1380.
[11]Zore Z, Filipovic Zore I, Matejcic A, et al. Surgical treatment of pathologic fractures in patients with metastatic tumors. Coll Antropol. 2009;33(4):1383-1386.
[12]张庆,刘傥,郭晓柠,等.瘤段切除灭活再植治疗儿童股骨恶性骨肿瘤[J].中南大学学报:医学版, 2013, 38(8): 843-846.
[13]徐敏,彭丹,彭红春,等.四肢恶性骨肿瘤保肢治疗的软组织修复及功能重建[J].中南大学学报:医学版, 2010, 35(3): 267-272.
[14]Liu T, Guo X, Zhang X, et al. Reconstruction with pasteurized autograt for primary malignant bone tumor of distal tibia. Bull Cancer. 2012;99(9): 87-91.
[15]Leckenby JI, Grobbelaar AO, Aston W. The use of a free vascularised fibula to reconstruct the radius following the resection of an osteosarcoma in a paediatric patient. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66(3): 427-429.
[16]史世勤,柴臻,同志超.股骨近端良性肿瘤骨缺损修复重建57例[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2011, 40(8): 1054-1055.
[17]胡孔足,卜海富.股骨近端置换术后应力分布和骨密度变化与个体特异性的相关性[J].临床骨科杂志, 2009, 12(1):37.
[18]冯乃清,路慎国,赫光栋,等.人工假体置换术治疗高龄骨质疏松性股骨颈骨折的临床护理模式及康复研究[J].中国伤残医学, 2013, 21(7): 84-87.
[19]石瑞梅.个体化护理干预对膝关节置换患者术后膝关节功能康复的效果观察[J]. 中国伤残医学, 2013, 21(7): 87-88.
[20]郭阗廷.人工假体置换在膝关节周围恶性肿瘤中的临床应用研究[J].实用中西医结合临床, 2013,13(7): 67-68.
[21]郭炜,李荣文,徐光辉,等.定制型人工髋关节置换治疗股骨近端瘤性病变[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006, 20(10):989-991.
[22]齐海,丁悦,许杰马,等. Harris评分和X线在评价全髋关节置换术后疗效中的作用[J].中华关节外科杂志, 2009, 3(4): 34-36.
[23]马琛明,陈彧,解基严,等.应用NHP量表评价糖尿病对冠状动脉旁路移植术后生命质量的影响[J].北京医学,2008, 30(8): 528-530.
[24]Stephen D. Management of Metastatic Osseous Lesions of the Lower Extremity. Techn Orthop. 2004;19(1): 15-24.
[25]周忠,陈学明,王万明.股骨近端骨肿瘤切除后特制人工假体置换[J].临床骨科杂志,2007, 10(3): 216-217.
[26]杨松华,符彦基,杨丹.股骨近端解剖钢板治疗股骨近端骨折[J]. 中国医疗前沿, 2009, 4(9): 32-33.
[27]施林军,张健,周爱国,等.人工髋关节假体在股骨近端转移瘤中应用13例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,19(9): 1747-1750.
[28]徐万鹏,徐绍年.带锁套筒式髓内假体在肿瘤性人工性膝关节翻修术中的应用[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病, 2008, 7(3): 149-151.
[29]裴国献,姜晓锐,魏宝富,等.前外侧肌间隙入路微创小切口全髋置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2010, 25(6):487-489.
[30]李建民,杨强.人工假体在骨肿瘤保肢术中的应用及发展[J].中国医疗器械信息, 2008, 14(11): 9-15.
[31]刘文广,李建民,刘凯红,等.定制肿瘤人工髋关节假体断裂三维有限元分析及套接式翻修假体的初步应用[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2008, 46(4): 431-432.
[32]Farid Y, Lin PP, Lewis VO, et al. Endoprosthetic and allograft-prosthetic composite reconstruction of the proximal femur for bone neoplasms. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2006; 442(1):223-229.
[33]赵洪普,徐秋玉,曾勉东,等.定制人工股骨头治疗股骨上段转移性肿瘤[J].临床骨科杂志,2012, 15(4): 376-378.
[34]赵洪普,徐秋玉,吕玉明,等.中老年人股骨上段恶性肿瘤人工股骨头置换治疗效果分析[J].临床外科杂志, 2012, 20(10): 732-733.
[35]毛宾尧.人工髋关节外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2002: 646-650.
[36]鲁珊珊,王德杭,李永军,等.全身MRI与核素骨扫描对骨转移瘤诊断价值的对照研究[J].中华放射学杂志, 2011, 45(5): 459-462.
[37]李莹,任翠萍,程敬亮,等.骨肉瘤的X线、CT及MRI比较分析(附61例分析)[J].放射学实践, 2011, 26(11): 1197-1200.
[38]高明忠.人工全髋关节置换术治疗股骨近端骨肿瘤的疗效及预后[J].中国肿瘤临床与康复, 2013, 20(7): 715-717.
[39]陈志伟,邓焱,侯子鑫,等.定制人工肱骨头假体置换治疗肱骨近端骨肿瘤的疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013, 27(4): 511-512.
[40]沈延东,郑慷.人工全髋关节置换术治疗股骨近端骨肿瘤早期疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011, 25(1): 120-122. |